This uniquely crafted article serves as your time capsule into the world of one great thinker - Socrates. Strap in as you are about to embark on a fascinating journey exploring the rich tapestry of this renowned philosopher's life, his profound philosophy, and his ongoing influence decades after his presence.
Socrates, considered by many to be the father of Western philosophy, has significantly shaped how we perceive the world around us today.
His philosophical principles based on relentless inquiry and logical argumentation pioneered a ground-breaking approach that allowed questioning conventional morals, virtues, and wisdom itself.
Who Was Socrates? Life and Philosophy of Socrates
Socrates, an eminent figure in Western philosophy, was a classical Greek philosopher praised for his profound insight into ethics. His philosophical views were primarily based on personal inquiry rather than established doctrine.

His Early Years
Born around 469 B.C. in Athens, Greece, Socrates' life is perceived through the works of historical figures like Plato and Xenophon, as he himself left no writings behind. His father Sophroniscus was a stone mason and his mother Phaenarete was a midwife.
Despite not being from a particularly affluent background, Socrates grew up to become one of the most influential thinkers the world has ever known.
As per Aristophanes' portrayal in "The Clouds", it is believed that Socrates started as a stone mason following his father's footprints and later dedicated himself entirely to philosophy. His approach towards knowledge and truth was shaped by the vibrant intellectual atmosphere of Periclean Athens.
The Importance of Socrates' Philosophy
Socratic influence pervades traditional philosophic thought. A few pivotal aspects birthed from his wisdom include:
- Questioning Established Knowledge: He urged people to challenge existing ideas instead of accepting them blindly.
- Understanding Life: He brought philosophy down from heaven to earth by insisting on human understanding and ethical matters.
- Focus on Ethics: For him, moral goodness stood paramount over all other dimensions.
His emphasis on self-growth through mindfulness resonates even today—the 'know thyself' principle encourages self-inspection for enhanced personal growth.
Equally significant is Socratic irony underpinning discourse through professing ignorance or feigning naiveté fostering an environment for ideological growth and exchange.
Many educators today still employ the 'Socratic method,' grounded in cooperative argumentative dialogue between individuals for stimulating critical thinking—it's lauded as one facet that stands testament to his enduring influence in educational paradigms.
Understanding the Core Aspects of Socratic Philosophy
When one examines the monumental contributions of ancient thinkers, Socrates holds an undeniably esteemed position. The ideas he developed, and the methods he employed continue to significantly shape philosophical thought and discourse.

Deeper insight into his philosophy allows us to understand how his unique perspective revolutionized many established notions.
The Development of Reasoned Argument in Socratic Philosophy
The philosophy of Socrates is uniquely underpinned by the development of reasoned argument. He introduced a structured framework for disputing suppositions and dissecting complex concepts.
- He believed in using reason and logical discourse as a means to pursue truth.
- His approach was founded on questioning conventional beliefs, thus encouraging critical thinking.
- By this, he challenged preconceived assumptions, forcing individuals to rethink their position.
Through this focus on reasoned arguments, Socrates transformed philosophical discussion into a potent avenue for intellectual stimulation and societal advancement.
The Oracle and its Influence on Socrates
Among several events from his life that had profound reflection on his philosophies was an incident at the Oracle of Delphi which claimed that no individual was wiser than him. This declaration altered not just how others perceived him but also how he began perceiving himself.
- This claim confounded him initially as he did not reckon himself as being very wise.
- It struck a chord within him, leading to detailed introspection regarding wisdom's true nature.
- Ultimately it prompted him to realize that wisdom lies in acknowledging one's ignorance or limitations in knowledge rather than overstating one’s understanding or proficiency about something unknown or partially known.
This encounter with the Oracle tremendously shaped his subsequent philosophical journey making humility an integral aspect in pursuit of wisdom.
The Concept of Virtue in Socratic Ideology
A central tenet of Socratic philosophy involves a deep emphasis on virtue ethics:
- In the Socratic belief system, Virtue was proposed not just as an abstract idea but as the basis of a fulfilled and meaningfully rich, ethical life.
- Wisdom and knowledge were seen by him as prescripts for virtuous behavior.
- He championed the idea that "one who knows the good, does the good."
This clear association he made between wisdom, virtue, and ethical living has been pertinent in shaping subsequent Western moral philosophy.
Also Read: Aristotle | Biography, Life, Work, Philosophy, and Thoughts
The Unforgettable Methods and Schools Of Thought Related To The Great Philosopher
There is no doubt that Socrates was a figure of significance in the realm of philosophy. His unique methodology for articulating philosophic discourse and contributions to various philosophical schools of thought forever changed the face of intellectual thought. Let's delve into some of these iconic elements related to Socrates.
Socratic Method Of Philosophical Inquiry
The 'Socratic method' is one name that rings aloud whenever the subject of philosophy is broached, and for good reason: it was a revolutionary approach in the world of knowledge inquiry. Here's what you need to know about it:
- The Socratic Method, typically applied in law schools today, was born out of Socrates' approach to facilitate learning through questioning.
- This method fundamentally involves a cooperative argumentative dialogue between individuals, based on asking and answering questions.
- It seeks to stimulate critical thinking and illuminate ideas by distinguishing between what we think we know and what we actually know.
Understanding Pragmatism- A Significant School Of Thought
Pragmatism is another significant school associated with this great philosopher. Below are some key aspects tied to this school:
- Pragmatism essentially emphasizes practical application over abstract principles.
- Rooted in action rather than speculation, pragmatists argue that the value or truthfulness of an idea or theory lies solely in its useful applicability.
- It was believed that Socrates exemplified pragmatism through his unyielding quest for practical wisdom in navigating ethical conundrums.
These methods exemplify just how innovative a thinker he was - leaving behind assets that philosophers still utilize today.
Political Turmoil During The Era: Its Relation with Socrates’ Life Course
In the exploration of Socrates' life and wisdom, it is crucial to understand the tumultuous social and political environment of Athens during his time. The machinations of Athenian politics, along with the subsequent trial, would have a profound influence on his philosophy.
Athens And Its Politics: How It Relates With Socratic Exemplary Wisdom
In order to fully apprehend Socrates's wisdom, it is key to delve into the intricate relationship he had with Athens’ inhospitable political climate. The city was at its apex during his life, a golden era for profound thinkers. However, this landscape was also associated with bouts of political upheaval:
- Power struggles: As democracy stood nascent in those days in Athens, intense power conflicts emerged that shaped public opinion.
- War prevalence: Trade wars and territorial disputes often took center stage over reasoning and philosophical debates, making it challenging for voices like Socrates' to be heard.
These shifts not only affected how Socratic philosophies were formed but also how they were perceived in society.
The Trial ‐ An Inevitable Conviction!
The turbulent political standpoint unsurprisingly resulted in a growing dissatisfaction among certain Athenians towards their celebrated philosopher - Socrates. His insistent promotion of critical thinking against popular belief made him an object of mistrust:
- Charge against corrupting youth: His unique pedagogical style was seen as undermining the established education system.
- Accusation about impiety: He questioned traditional religious beliefs which led authorities to take legal action against him.
This tumultuous background ultimately culminated in the unjust trial and conviction that marked a dark chapter in philosophical history. Socrate's wisdom was seen as defiling rather than enlightening due mainly to its being misunderstood within this conflicted socio-political context.
Thus, an understanding of Athens' political turmoil can shed more clarity on how the life course of Socrates and his philosophical endeavors were inexorably intertwined.
Socrates: His Obstinacy and Self-imposed Death
Even the most cursory reading of ancient history will reveal that Socrates was a man who remained steadfast in his beliefs until his very last breath. It is his unwavering obstinacy, ironically, which led to his self-imposed death, casting a haunting yet thought-provoking finale to his life's tale.
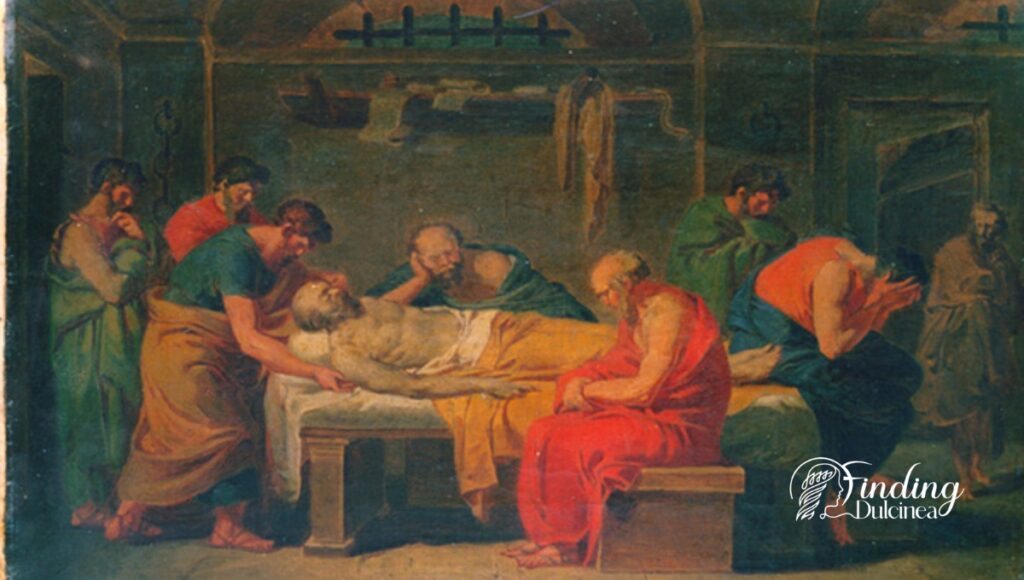
The Death of Socrates
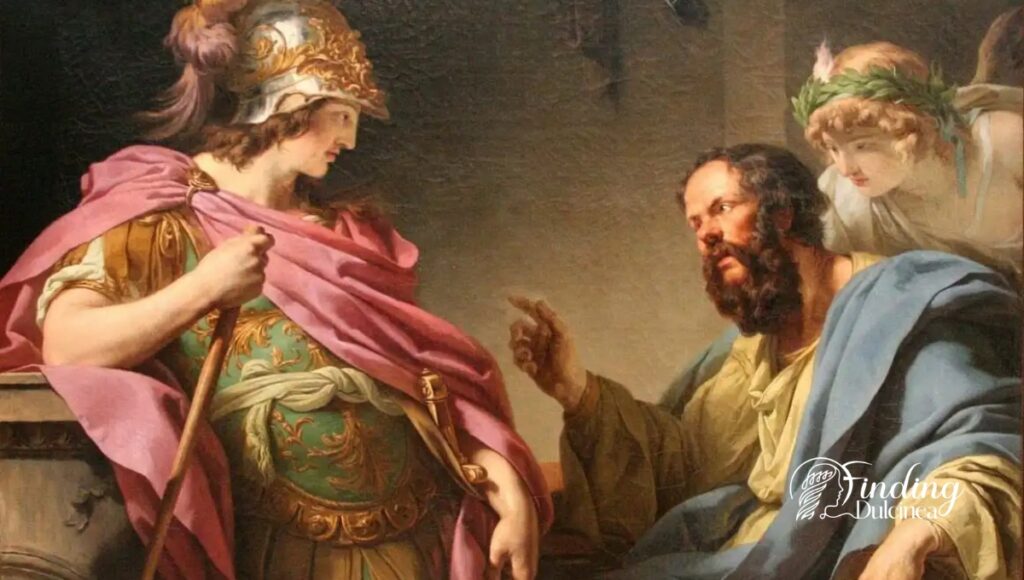

The account of the death of Socrates is often considered one of the most profoundly moving moments in ancient history. Despite an opportunity for escape-- offered to him by friends determined to save him from the Spartan prison he was held captive --Socrates chose otherwise. This decision highlights his obstinacy and unshakeable belief system.
- His reasons for refusing escape revolved around respect for Athenian law. He believed that executing an unjust command would result in ruining one's character.
- Secondly, escaping would imply that he lived in fear of death; contrary to everything he had preached about not fearing what one did not understand.
- Lastly, Socrates thought that escaping constituted repaying harm with harm - something against his principles.
It was here, ushered by dawn on a fateful day in 399 BC when the philosopher stoically embraced death. With trusted friends at hand and sadness prevailing heavily through tear-laden eyes among those who bore witness, Sóracles obediently swallowed hemlock—a powerful neurotoxin—to meet with eternal silence.
Socrate's willingness to face execution portrays how much value he placed on maintaining character integrity over life preservation. This defining moment casts light upon how succumbs only bore forth from an immersive stubbornness convincingly embedded into seeking truth.
A trait is notoriously challenging yet truly vital in shaping up commendable societal templates conscientiously expanding human wisdom horizons thenceforth till perpetuity ignited via often recalled tales spun off our long lost yesteryears healing melancholic sages from their mundane torment.
Also Read: List Of 12 Greatest Greek Philosophers Of All Time
FAQs
What was Socrates famous for?
Socrates was famous for being one of the founding fathers of Western philosophy. He is best known for his way of questioning and the Socratic method.
What are the three ideas of Socrates?
The three significant ideas attributed to him include: knowledge is a virtue, one must understand oneself, and it is important to question life's big issues.
Who loves Socrates?
Those who enjoy philosophy and value critical thinking hold a deep respect and love for Socrates. Students, educators, philosophers, and anyone seeking wisdom are often admirers of his work.
Conclusion
It remains unequivocal that Socrates was indeed a revolutionary figure. His contributions to philosophy, ranging from his reasoned arguments to his unique method of inquiry, were fundamental in constructing how thought and wisdom are perceived today.
His rebellious spirit against Athenian politics led to his tragic end but ultimately, it amplified his indomitable principles. The Socratic legacy continues to influence thinkers worldwide, substantiating the importance of questioning prevailing knowledge and uncovering deeper truths.
With his courageous approach towards life and unabashed pursuit of knowledge, Socrates has undyingly engraved himself in the annals of history.
Monika Soni is a passionate writer and history enthusiast who joined the FindingDulcinea team in July 2023. With a deep love for both ancient and political history, she brings a unique perspective to her articles, weaving together narratives that captivate and educate her readers. Monika holds a B.Sc. degree from the esteemed Govt. College of Girls, Panchkula. When she's not diving deep into historical research, Monika enjoys exploring local museums and historical sites. Her commitment to bringing history to life makes her a valuable asset to the FindingDulcinea community.
