In the sunlit lands of Spain, a tale as old as time whispers through the ages—a story where brave warriors and shrewd kings fought for their homes. This is not just any tale; it’s our shared human saga of triumph and resolve that spans centuries.
Imagine the Reconquista, an awe-inspiring era when Christian kingdoms valiantly rose to reclaim the Iberian Peninsula from Moorish rule. As we delve into this historical period, prepare to be transported back to medieval Spain—where faith, power, and destiny collide in a relentless struggle for supremacy.
When we explore what happened during those transformative years of Reconquista, we see a dramatic shift in power unfolding across Spain. The Christians moved from the mountain fringes to recapture lands held by the Moors for over seven centuries.
Each battle added another layer to this complex historical tapestry, marking milestones that eventually led to a united Spanish kingdom under Ferdinand and Isabella. It was a journey marked by bloodshed yet driven by aspiration—a sweeping change restoring the presence of Christianity across Spain.
Understanding Reconquista: A Quest to Reclaim
Our journey through history takes us back to a time we call the Reconquista, a time of mighty battles and bold warriors. Over many years, Christian kings fought to take back Spain from the Moors, who were Muslim folks from North Africa.

The Early Stages of Reconquista
It all started long ago in the year 711 when Moorish soldiers crossed the sea and won a big fight against the Spaniards in a place called Guadalete. After this battle, they took control over much of Spain. This was not something the Christian kings liked very much. What sparked off our Reconquista story was not just one event but many little moments that made Christians want their land back.
One special day marked the beginning of this plan to retake Spain—a brave man named Pelayo stood up against the Moors in a small part of northern Spain called Asturias in 718 or so. This Battle of Covadonga wasn’t very big, but it meant a lot because Pelayo and his men were victorious. People say this win started our long quest—the Reconquista.
Years went by, and different Christian lands joined together to fight back against their Moorish rulers. The lands had leaders like Alfonso VI, who took over Toledo in 1085, and the famous El Cid, who fought bravely around Valencia.
Each step forward for these Christian soldiers was tough but gave them hope that they could reclaim their entire homeland one day. They believed God wanted them to have these lands again.
The Cultural Tapestry of Medieval Spain
The Moors stayed for hundreds of years before our tale’s end, so they left behind a great mix of art—beautiful buildings like the Alhambra palace with its fine decorations—and new ideas about science and medicine too.
In every corner—from cities filled with marketplaces where people traded goods from far away places to farms growing tasty fruits—we found hints that Spanish life under Moorish rule was full of different cultures living side by side:
- Christians kept going to church and living as they always had as much as possible.
- Muslims followed the Islamic teachings brought over by those Moroccans across that sea.
- Jews worked as doctors or tradesmen—a big part of our story since they helped both Christians and Muslims alike!
Together, all these people made Medieval Spain shine bright like nowhere else—a place where books were written about stars far above or plants growing down below, mixing thoughts from each community into something grand!
Spain’s music changed with new sounds echoing through halls; food cooked in kitchens smelled better with spices no one knew before; words spoken on streets sounded smooth like silk because they got mixed up from everywhere!
Even though fights happened—like any family squabble—during peaceful times, folks shared stories under starry skies, dreaming about what could be if only everyone got along together forevermore.
It’s this colorful weave—an ever-changing picture—that reminds us how much humans can create when we open doors instead of closing them tight out of fear or hate.
Also Read: Who is Hera in Greek Mythology?
Key Battles and Turning Points in Reconquista
The Reconquista was a series of events where Christian kingdoms aimed to take back Spain from the Moors. This long fight included many battles with turning points that changed the course of history.
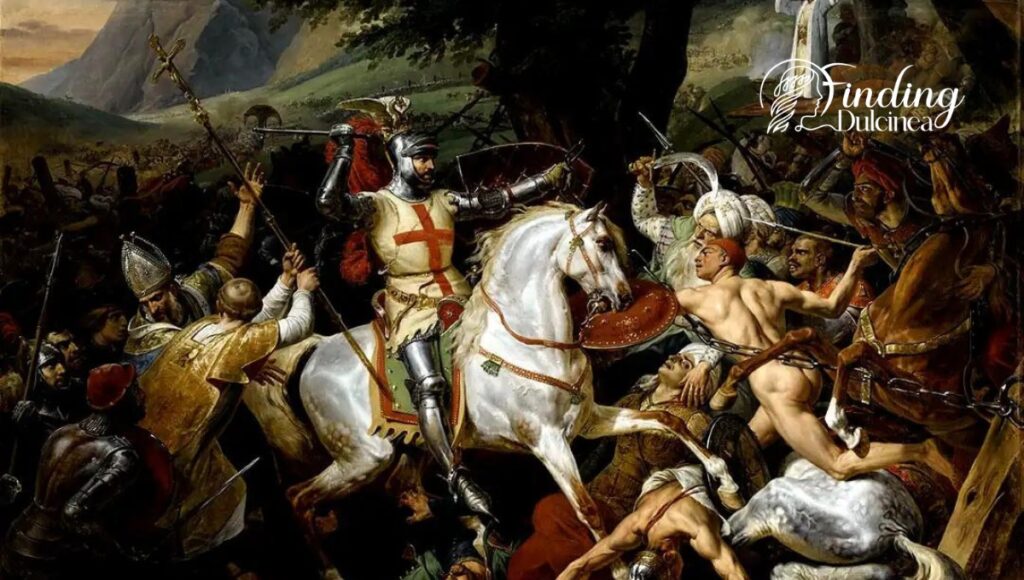

Conquest of Toledo: Gateway to Central Iberia
In May 1085, a big change came when Christians took over Toledo, a city in central Iberia. Below is how it happened:
- Who? King Alfonso VI of Castile led the Christian side.
- Why Important? Toledo was once a big city for learning and culture. It was also in the middle of Spain, which made it very key for control.
- How? The siege. Alfonso’s army surrounded Toledo and cut off supplies until they gave up.
- End Result: After this battle, Christians had a stronger hold in central Spain. It was like opening a door to more lands for them.
Toledo’s fall meant more than just winning land. It signaled that the Christians could beat the Moors and maybe one day control all of Spain.
Role of El Cid in Spanish Lore and Reality
El Cid is both a hero from stories (lore) and a real person who fought in battles. Let’s dig into his role:
- Who Was El Cid? His real name was Rodrigo Diaz de Vivar—a strong warrior born near Burgos.
- His Deeds: As both leader and fighter, he won important fights like against foes at Valencia.
In tales (lore), El Cid almost has superpower-like abilities. People see him as very brave and wise—a symbol of good against evil during those times.
But even in real life, his actions had big effects on the fight between Christians and Moors:
- He brought together his own army, which didn’t always follow one king or kingdom.
- With his force, he took over Valencia—a major coastal city—and ruled there till he died.
- His life helped inspire poems and stories, which boosted people’s spirits during tough times.
El Cid remains an icon with tales spreading far beyond just history books but into movies, plays, arts – you name it!
So here we have seen why Toledo’s taking meant so much and how both fact and legend mix to make El Cid an everlasting part of Spanish culture during these Reconquista years.
Also Read: Who Was Aphrodite?
Dynamics of Power Among Christian Kingdoms
When we speak of the Reconquista, the tale of how Spanish Christians took back their lands from the Moors, we look at a tapestry woven with strife, strategy, and shifting dominions. This was a time when power was hard-won and fleeting, depending on alliances made not just on the battlefield but also through bonds sealed by marriage vows.
Rise of Aragon and Castile
Amidst this complex backdrop emerged two formidable powers: Aragon and Castile.
- Aragon, nestled by the shimmering Mediterranean Sea, gained its strength from shrewd commerce and maritime prowess. Its kings expanded their territories through strategic alliances.
- Castile rose from an inland region to prominence under enterprising leaders like King Fernando I. Castilian influence spread far thanks to military conquests.
- The union between these kingdoms came through a wedding between Queen Isabella of Castile and King Ferdinand of Aragon. Together, they formed a coalition that would alter the course of Medieval History on the Iberian Peninsula.
- Their joint rule not only cemented control over their respective realms but also marked a turning point in the Reconquista efforts against Moorish states.
By joining forces both in matrimony and in warfare, Aragon and Castile became beacons around which other Christian forces would rally as they advanced upon Moorish-held territories.
Politics & Warfare Strategies During Reconquista
The flow of power during the Reconquista was changing much like swift currents in stormy seas; politics was intricate while warfare strategies were ever-evolving.
- The chessboard that was Spain saw kings making moves by building alliances with other realms for mutual benefit.
- Treaties were signed and then broken; loyalty shifted depending on who held favorable positions both geographically and politically.
- In military terms, Christian armies adopted various tactics, such as hit-and-run raids or prolonged sieges, to reclaim swathes of land bit by bit.
- They ensnared Moorish fortresses using strategic cunning — enticing defections or launching surprise attacks at weak points illuminated by thorough reconnaissance.
At its core, what propelled these kingdoms toward success wasn’t just brute force but also an immense grasp on political dexterity matched with relentless military innovation. Through piece-by-piece recapture of terrain accompanied by tactical diplomacy, they pursued their singular goal: taking back Spain.
Also Read: Who Was Roman Emperor Caligula?
Unification Under Ferdinand and Isabella
In the echoes of medieval history, a single union brought forth the birth of what would become modern Spain. We must travel back in time to fully grasp the monumental impact of a marriage between two royal figures that shaped a nation and altered the course of historical events in Europe.
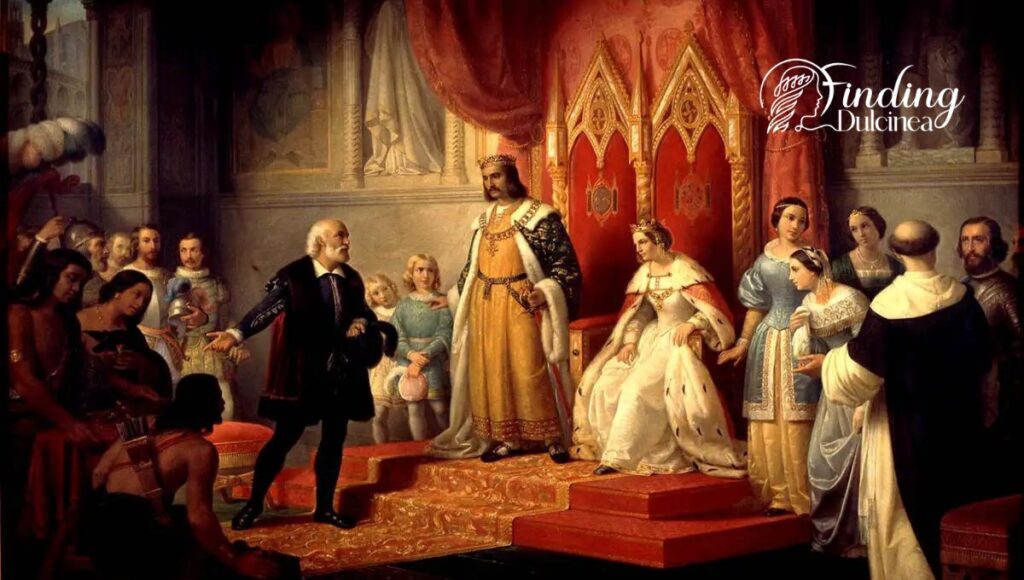

Marriage That Created a Superpower
Imagine two kingdoms, each holding their own power and influence. In one corner stood Aragon with its ruler, Ferdinand II, and in the other lay Castile, under the rule of Isabella I. Their marriage in 1469 was not just your typical royal wedding; it was a strategic alliance that cemented their status as power players on the Iberian Peninsula.
Before we dive deep into their story, let’s get this straight: back then, kingdoms were like chess pieces, always moving to win more power. So, when we talk about Ferdinand and Isabella tying the knot, we are looking at a game-changing move. The joining of these two rulers through matrimony did so much more than unite hearts – it united lands under one banner.
Here’s how it went down:
- Ferdinand hailed from Aragon – think eastern Spain with Barcelona as its crown jewel.
- Isabella, on her side, brought Castile to the table — an area covering central and northern Spain.
By coming together in marriage, these love birds did not just share sweet nothings but combined their strengths to wield greater control over territories throughout Spain. It meant they could pool resources together, whether it was knights or gold coins.
With both crowns now sitting snugly on their joined heads, so to speak – thanks to this marital mega-deal, if you will – they set out on ambitious conquests that would change things big time for everyone living on what was known as the Iberian Peninsula during those days.
This alliance stamped out internal disputes — no more bickering between neighboring royals — allowing them to focus outward on bigger fish… or rather realms left held by others who didn’t exactly share their vision for unity under Christianity (yep, talking about Moors here).
Completion of Reconquista Under Their Rule
1492, keep this year in mind because that’s when Ferdinand and Isabella crossed off a massive item from their royal bucket list — taking Granada back from Moorish control, marking an end to almost 800 years where different cultures threw punches over who gets to call Spain home.
Think big! Imagine bringing closure to a centuries-long chapter filled with battle after blood-soaked battles – this was momentous!
The nitty-gritty looks something like:
- The city of Granada stood strong against Christian forces for ages. It had walls built tough enough to make even seasoned knights think twice before trying anything funny.
- But our duo had something up their sleeves – patience, and strategy mixed with downright grit! They tightened up around Granada like how you’d close drawstrings around a bag until there wasn’t much wiggle room left inside.
- Then came surrender negotiations: tense talks trying to figure out safe exits without too much fuss or muss from either side because, hey, no one wants unnecessary drama, right?
- Finally, terms were agreed upon…and voilà! January 2nd rolled around waving bye-bye to Moors’ rule hence finishing the reconquest chapter once all is said and done sealed, and delivered!
Their victory at Granada wasn’t just some military badge they got pinned; it signalled hope for supporters aiming for Christian-dominated reign across the realm whereas others saw days ahead filled with worry wondering what come next especially considering there were still many peeps living there practicing Islam Judaism having done so generations upon generations…
The aftermath included edicts flying left right center aiming to reorganise society according to newly established norms which, let’s be honest wasn’t all roses and sunshine especially those end receiving stick rather than carrot treatment.
Weaving through our story is a key takeaway folks – marriage can indeed be a powerful thing when aims merge raising stakes higher than personal gain paving the way towards history books that get frequently revisited even into our present day thousands of years later!
Also Read: All About Moros: The Greek God & Goddess of Impending Doom
Aftermath of Reconquista: Shaping Modern Spain
The Reconquista was not just a series of battles; it completely changed how Spain looked and felt. After the Christian kings won back land from the Moors, they did many things to make sure their power stayed strong. They wanted everybody to know that Spain was a Catholic country now.
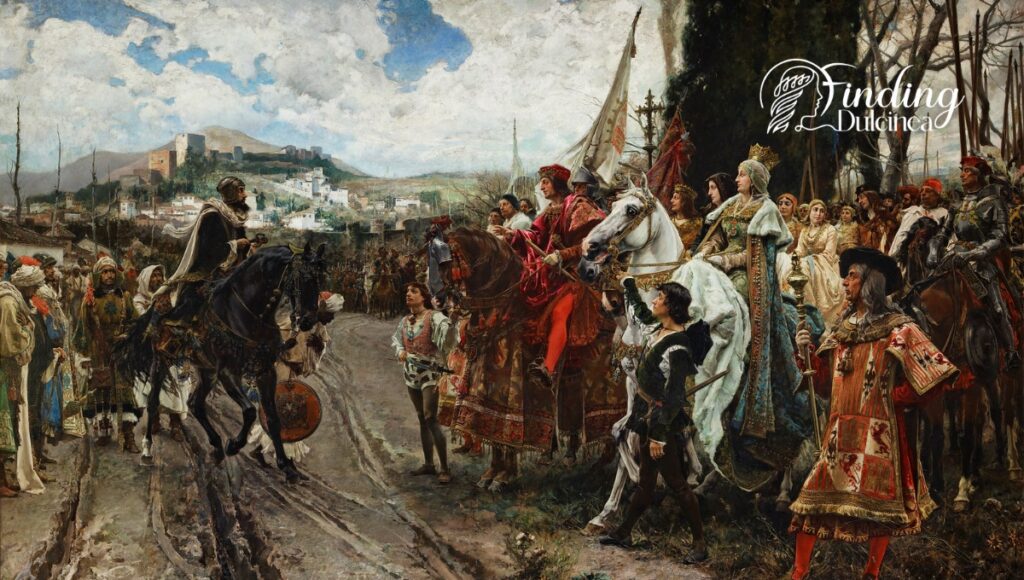

Establishing a Catholic Kingdom
In the years that followed, the leaders of Spain worked hard to build a kingdom where everybody was Catholic. This was very important for them. Churches were built all over the place, and priests became powerful people in towns and cities.
Spanish kings like Ferdinand and Isabella said everyone in Spain had to be Catholic. This meant that people who had other religions—like Muslims or Jews—had to either become Catholics or leave Spain. Many left because they did not want to change their religion.
Our cities started looking different too—big cathedrals reached up toward the sky, showing off how important Christianity was. The crosses everywhere reminded us who was in charge now—that this land belonged to Catholics.
The Commitment to Religious Purity
Kings wanted everybody to be true Catholics; they didn’t trust anyone who changed their religion just because they had to. To keep an eye on this, something called the Spanish Inquisition started.
The Inquisition had people called “inquisitors” looking into everyone’s business, making sure they were real Catholics. These folks would watch you pray and check if you knew about Jesus and Mary properly.
If someone still practiced old Jewish rituals or Muslim prayers secretly—they could get in big trouble! We’re talking scary stuff like being put on trial or even worse punishments—which we don’t need to talk about here!
Neighbors began spying on each other out of fear or sometimes because they didn’t like someone; if someone got told on for not being a good enough Catholic, it meant big problems for them!
Everyday life for us got nerve-wracking—you always had to show how good of a Catholic you were so nobody would suspect anything else.
Being part of our community meant following these rules strictly—we all felt the weight of this new order pressing down on us since staying safe meant toeing the line carefully at every turn.
The Widespread Impact of Reconquista on Global Politics
The Reconquista stands as a pivotal point in our history, a grand saga of battles and beliefs that reshaped not only the Iberian Peninsula but also sent ripples across the globe that could be felt for centuries.

As we look back at those tumultuous times, we can’t help but marvel at how this monumental conflict influenced international affairs and redefined political alliances everywhere it touched.
When we think about the Reconquista, what rings most significant is its undeniable influence on political relationships within Europe and across the Mediterranean.
As Christian kingdoms in Spain fought to reclaim lands from Moorish control, it wasn’t just a local skirmish – it was like shaking a vast spider web, each strand vibrating with tension felt all over.
European powers were drawn into this fray either directly or as crafty spectators looking to benefit from whichever side might emerge victorious. Over time, alliances shifted; old enemies became new friends if it meant an advantage against Moorish power in Spain. Kingdoms like Aragon and Castile sometimes put their quarrels aside to face their common foe together.
With each victory against the Moors, these Christian states grew more robust and self-confident – they began to see themselves not as scattered kingdoms but as united Spaniards with shared goals.
This feeling carried over when dealing with other nations; now they negotiated treaties and trades from a position of enhanced prestige and strength.
But let’s not forget about those across the Mediterranean. North African Muslim states watched anxiously as their brethren’s grip on Spanish lands slipped away. Alliances across this great sea also started shifting as some sought to maintain ties with emerging Spanish power while others doubled down on resistance.
We need only glimpse back at this era’s diplomatic chessboard to witness how profoundly tensions wrought by our Reconquista journey transformed Europe’s very identity.
Expansionism and Exploration
In the aftermath of the Reconquista came an intense period where Spain surged forth into a golden age of exploration and colonization – fueled by fresh national unity. With Muslim rule expelled after nearly 800 years, there was now fervor for new frontiers both spiritually motivated (to spread Christianity) and driven by dreams of wealth.
That sense of ‘oneness’ which had slowly stitched together during countless battles translated into an ambition too massive for just one continent. The daring voyage taken by Christopher Columbus in 1492 under Spanish patronage wasn’t merely a search for trade routes; it was emblematic of Spain’s larger mission to plant its flags upon uncharted territories far beyond European shores.
Spain’s expanding ambitions paved the way for unparalleled maritime exploration as they pursued empire-building on an epic scale – far-reaching expeditions led by names such as Hernán Cortés and Francisco Pizarro followed suit who carved out colossal swathes of territory across the Americas for their homeland.
We can’t overlook that this thirst for conquest brought profound suffering through wars upon indigenous peoples – yet these very acts created complex new societies while luring European rivals into similar quests overseas seeking their fortunes among foreign lands.
Such was Spain’s hunger born out of newfound unity post-Reconquista; it propelled them onto global stages where they would influence cultures vastly different from any rolling hill or sun-baked plain back home.
Also Read: Were Ancient Egyptians Black?
Reflections on Tolerance and Coexistence Post-Reconquista
Once upon a time, our home, the Iberian Peninsula, was a land where many different people lived together. Christians, Muslims, and Jews called this place home and shared their lives with each other. However, that all changed after the Reconquista. This was when Christian kingdoms took back Spain from the Moors.

A Tale of Two Periods: Convivencia vs. Post-Reconquista Tensions
Before we dive too deep, let’s set the stage:
- Convivencia means “living together” in Spanish.
- During this period on the Iberian Peninsula:
- Christians, Muslims, and Jews lived side by side.
- They traded with each other.
- They learned from each other’s cultures.
- And they added to our rich history through their cooperation.
Now let’s contrast this with what happened during Reconquista:
- The Reconquista was a long conflict spanning hundreds of years.
- It ended with Christian kingdoms taking control over all the lands once held by Muslims.
- After the Reconquista succeeded:
- There was forced conformity – people had to follow one religion.
- Those who weren’t Christian faced a tough choice: convert or leave.
Our past is like a colorful mosaic made of different pieces. When those pieces were taken away or forced to change after the success of the Reconquista, that mosaic lost some brightness.
The contrasts between these periods show us lessons about tolerance and how important it is for peace. We come closer to understanding not just our past but ourselves when we reflect on both eras.
Evaluating Historical Narratives
When we open history books or listen to stories about our past — particularly about something as massive as the Reconquista — it shapes how we see ourselves today.
To understand better:
- Historical narratives are simply stories from our past that people tell in various ways based on what they think is important.
In terms of evaluating these narratives related to the Reconquista:
- Different Interpretations:
- Some people might see it as a heroic fight for homeland retrieval by Christians.
- Others consider it an era that brought an end to centuries of rich cultural diversity and learning.
- Impact On Cultural Identity:
- For many Spanish folks today:
- These stories help them find pride in their heritage.
- Yet others might feel sadness over what got lost during those changes.
Examining these historical narratives makes us question :
- How do we reconcile pride in our nation’s achievements with recognition of its losses?
It’s crucial for us not just to remember tales told from only one point of view but also acknowledge multiple perspectives that create our complex cultural identity tapestry.
By paying close attention (without growing bored or repeating ourselves), we start understanding more than just facts; we grasp emotions woven through Spanish life threads over generations.
After all, history isn’t only about wars and treaties – it’s also about hearts and dreams shaped through time under Iberia’s sunlit skies–and dark periods too.
Conclusion
Our journey through the Reconquista reveals a mosaic of ambition, clash, and transformation on the Iberian Peninsula. We have traversed pivotal moments that not only altered the fabric of Spain but left a lasting imprint on world history.
This medieval saga unfolded over centuries, with both dramatic military engagements and gradual societal evolutions painting the backdrop for a newly unified Spain.
Anne Kostick has been Editor-in-Chief since September 2007. Previously, Anne was a principal at Foxpath IND, a publishing, consulting and editorial services company specializing in the transition to and from traditional content publishing and online content management, development and publishing. Her clients included trade book publishers, technology and financial services Web sites, and arts and cultural institutions. Previously, she worked as Licensing and Product Development Director, Senior Acquisitions Editor and Director of Electronic Publishing for Workman Publishing, and as Senior Acquisitions Editor for Harry N. Abrams/Stewart, Tabori & Chang. In the online world she worked as Director of Content Development for Vitaminshoppe.com. Anne has a B.A. in Greek and Latin, with a minor in Theater, from Beloit College. She is the author of several books for children, as well as a definitive collection of jokes.
